Consuming too many highly processed foods, refined sugar, and saturated fats promotes the accumulation of fat in the liver. The main culprits are sodas, processed foods, and baked goods with high sugar content!
Overweight and obesity
Obesity, especially in the abdominal area, is a major risk factor. Obesity promotes inflammation and insulin resistance, which disrupts lipid metabolism in the liver.
Alcohol, an enemy of the liver
Regular and excessive alcohol consumption impairs the liver’s ability to metabolize fats, which can lead to alcoholic fatty liver disease.
Diabetes and metabolic syndrome
People with type 2 diabetes, high blood pressure, or high cholesterol are more likely to develop fatty liver disease. These disorders disrupt fat metabolism and promote their accumulation in the liver.
A special case: fatty liver during pregnancy
Some pregnant women may experience acute fatty liver disease of pregnancy, a rare but serious condition that requires immediate medical attention. Fortunately, it usually resolves after delivery.
What are the symptoms?
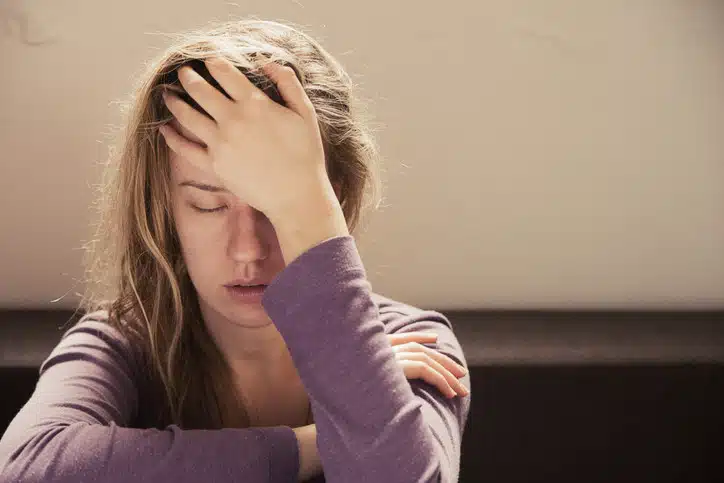

Fatty liver disease is often asymptomatic, but certain signs should alert you:
- Persistent fatigue
- Right-sided abdominal discomfort
- A general feeling of discomfort
- Jaundice (yellowing of the skin and eyes, an advanced sign of the disease)
If these symptoms occur, it is essential to see a doctor for a liver examination.
How can fatty liver disease be prevented and treated?
The good news: A healthy lifestyle can prevent or even reduce fatty liver disease! Here are the most important steps you should take.